The role of data in Measuring Performance is both operational and transformational. The roles unfolds across key dimensions like:
1. Objectivity & Evidence-Based Evaluation.
Data removes guesswork and bias, offering quantifiable proof of progress or gaps.
– It enables fair comparisons across individuals, teams, or institutions.
2. Goal Alignment & Strategic Tracking.
Data links performance to strategic objectives, ensuring efforts are purposeful.
It helps monitor Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) and adjust tactics in real time.
3. Trend Analysis & Predictive Insights
Historical data reveals patterns. It shows what works, what doesn’t, and why.
Predictive analytics can forecast future performance or risks.
For example data is critical in analyzing training participation trends to anticipate future skill gaps in an organization.
4. Decision-Making & Resource Allocation.
Data informs where to invest time, money, and effort for maximum impact.
It supports evidence-based policy and program design.
5. Continuous Improvement & Accountability.
Data enables feedback loops for learning and growth.
It fosters a culture of transparency and responsibility.
6. Human Capital Optimization.
Data helps assess talent effectiveness, engagement, and development.
It supports strategic HR decisions like succession planning or leadership development.
For example data is handy when mapping employee competencies against organizational goals to identify training needs.
The importance of data across aspects indicates the role of research in an organisation.
Definition of Research
Research is a systematic, purposeful process of inquiry aimed at discovering, interpreting, and applying knowledge. It involves identifying a problem or question. Then, it includes collecting and analyzing data. Finally, conclusions are drawn to contribute to understanding, decision-making, or innovation.
Elements of Research
Research is characterist by these elements:
1. It is systematic
Research follows a structured plan or design
2. It is objective
Research seeks truth without bias
3. It is evidence-based.
Research relies on data and observation
4. It is analytical
It involves critical thinking and interpretation
5. It is purpose-driven
Research aims to solve problems, test theories, or generate insights
Certainly, John. Let’s take a deeper dive into the types of research. We will expand beyond the basic categories to provide a comprehensive, strategic, and context-aware understanding. This is perfect for guiding students, training educators, or advising institutional leaders.
—
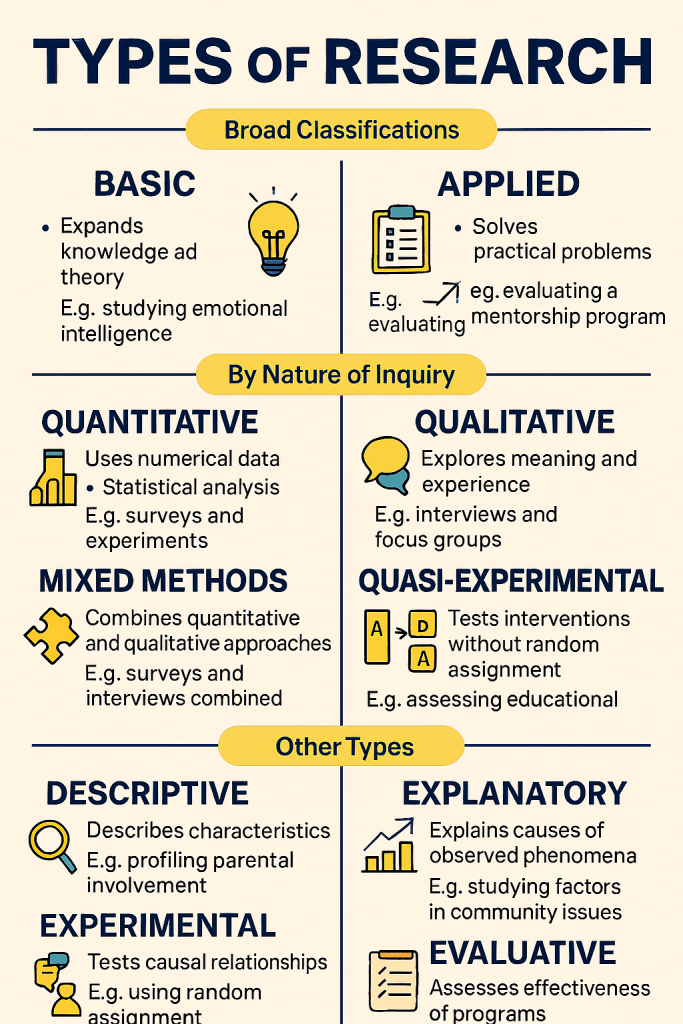
Classifications of Research
Research can be broadly classified into two categories:
1. Basic (Fundamental) Research
Basic research aims to expand theoretical knowledge without immediate application.
It focuses on understanding principles, concepts, and phenomena.
It is used in academic settings to build foundational theories.
An example of basic research is studying how emotional intelligence develops in adolescents.
2. Applied Research
This rearch solve specific, practical problems.
It’s focus is on real-world impacts and implementations.
It is ideal for policy development, program design, and institutional improvement.
Research can also by classified by Nature of Inquiry into:
a). Quantitative Research
This research aims to quantify variables and analyze relationships statistically.
It uses methods of inquiry like surveys, experiments, and structured observations.
It uses tools like SPSS, Excel, regression analysis for data analysis
It is best for measuring performance metrics, trends, and correlations.
b). Qualitative Research
The main purpose is to explore meanings, experiences, and perspectives.
It uses Interviews, focus groups, document analysis as methods of data collection
It applies tools like NVivo, thematic coding, narrative analysis for analyzing data.
This is a powerful type for understanding human behavior and community dynamics.
c). Mixed Methods Research.
This type combines the strengths of both quantitative and qualitative approaches.
It’s designs are sequential, concurrent, or embedded.
It is ideal for holistic evaluation of phenomenon.
Research can also be categorised by design into:
a). Descriptive Research.
The goal of descriptive Research is to describe characteristics or conditions.
b). Correlational Research
Correlation Research aims to examine relationships between variables.
For example exploring the link between Social Emotional Learning integration and student discipline outcomes.
c). Experimental Research.
Experimental research tests cause-effect relationships under controlled conditions.
For example randomly assigning students to different teaching methods to compare outcomes.
c). Quasi-Experimental Research.
This research is used to test interventions without full control or randomization.
Other Types of Research
a). Exploratory Research
It is used when little is known about a topic. It’s purpose is to generate hypotheses and insights for future studies.
b). Explanatory Research.
This research seeks to explain why or how phenomena occur.
It builds on existing knowledge to deepen understanding.
c). Evaluative Research.
This research evaluates the effectiveness, efficiency, or impact of programs.
It is common in policy analysis, education, and organizational development.
d). Action Research.
This research is collaborative and iterative.
It’s purpose is to solves real-time problems while generating knowledge.
In Summary
Basic research expands theory while applied solves real-world problems
Quantitative Research deals with numbers and statistics whereas qualitative research interrogates meaning and experience
Descriptive studies profiles characteristics, correlational examines relationships while experimental research tests cause-effect.

Leave a comment