Introduction.
Why does Performance Matter?
In every organization, the question of performance is inevitable. Whether we’re evaluating a student’s growth, a team’s effectiveness, or a program’s impact, performance stands as the ultimate outcome variable. Performance is the measurable result of effort, strategy, and context.
But what exactly is performance? How do we define it, dissect it, and measure it meaningfully?
What Is Performance as an Outcome Variable?
In research and strategic evaluation, an outcome variable is also known as a dependent variable. It is what we seek to explain or predict. Performance, in this context, is the observable result influenced by various inputs. These inputs are training, leadership, motivation, resources, and environment.
Performance is not just about results—it’s about the quality, consistency, and impact of those results.
Dimensions of Performance
Performance is multi-dimensional. The core dimensions of Performance used across sectors include:
1. Task Performance
It deals with the execution of duties and responsibilities. It looks at the accuracy, timeliness, and efficiency of executing those duties.
2. Contextual Performance.
This refers to the behaviors that support the organizational climate. They include cooperation, initiative, and adaptability.
3. Adaptive Performance.
It includes the ability to respond to change and uncertainty. Innovation, resilience, and problem-solving are key features of adaptability.
4. Learning & Development
This looks at growth in skills, knowledge, and capacity. It considers engagement in training, feedback, and mentorship within the organization
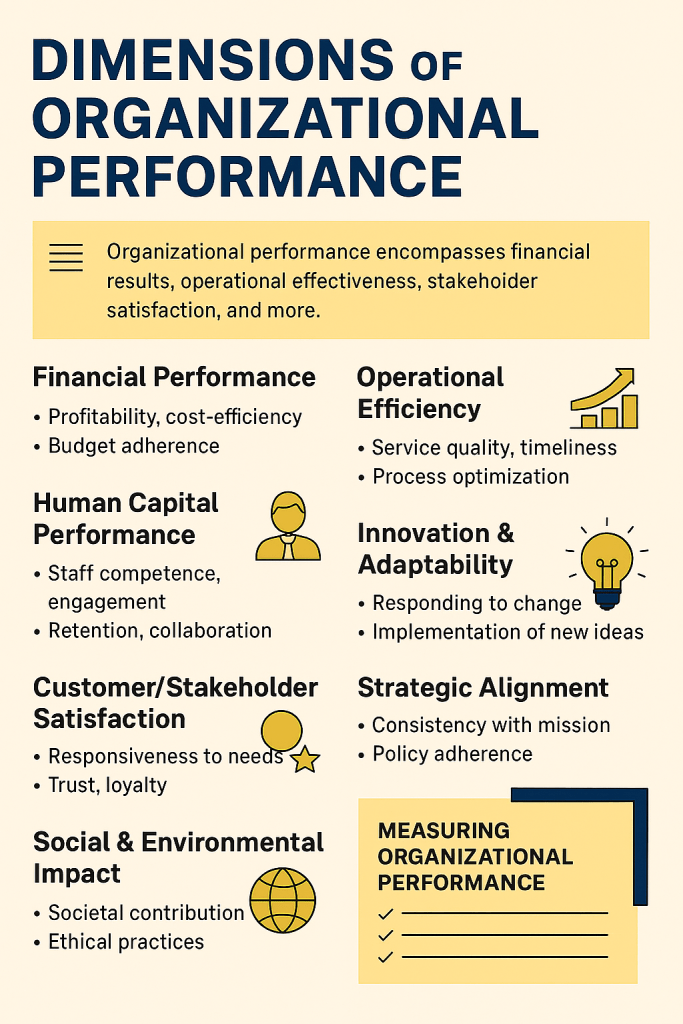
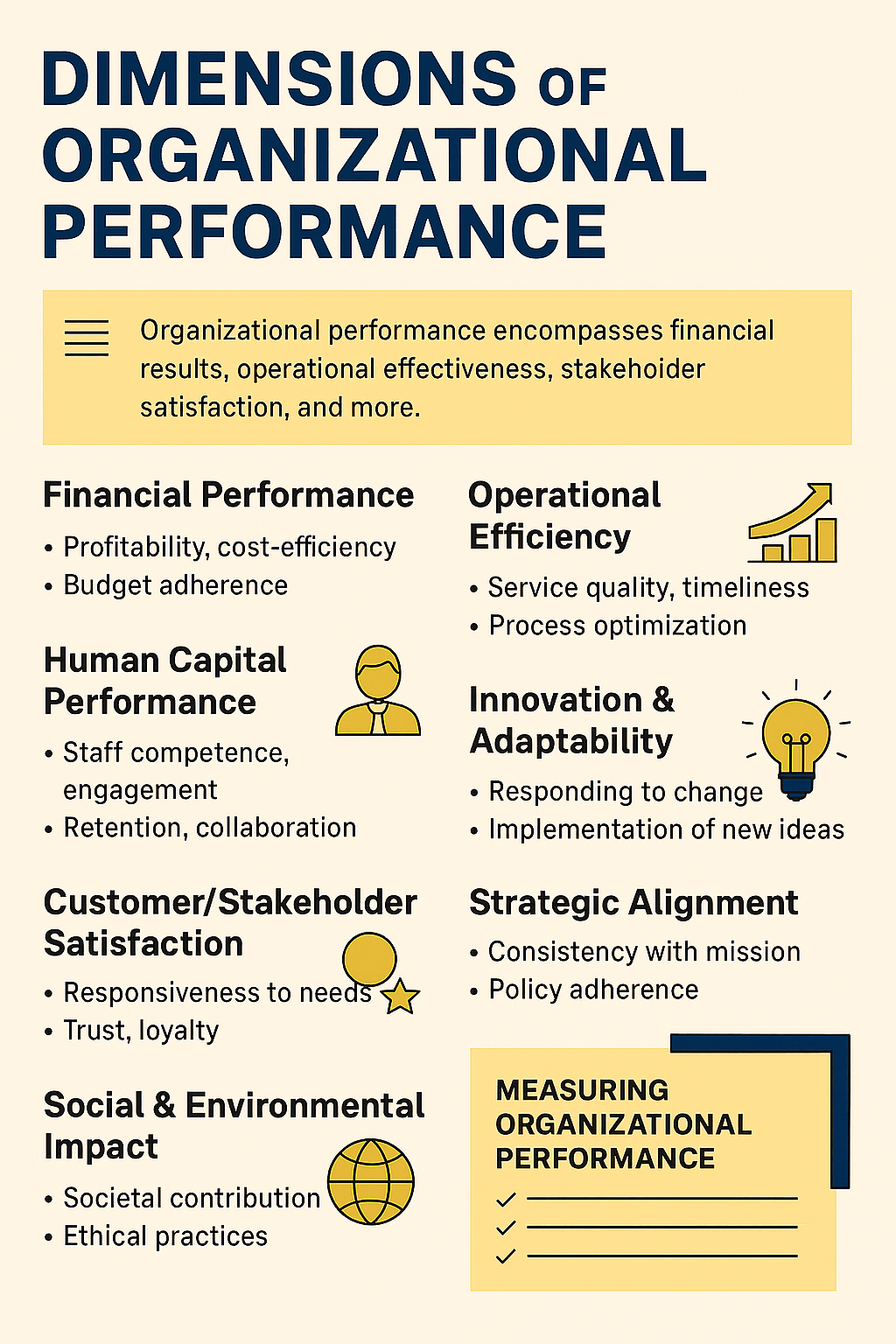
Dimensions of Organizational Performance
Organizational performance goes beyond financial results. It reflects how well an institution fulfills its mission, adapts to change, and delivers value to its stakeholders. In any contexts, performance must be viewed holistically.
Dimensions of organizational Performance include:
1. Financial Performance
This aspect deals with firm profitability, cost-efficiency, and return on investment. It also looks at budget adherence and resource stewardship
2. Operational Efficiency
Effecience deals with quality and timeliness of service delivery. Process optimization and waste reduction is also another aspect of efficiency.
3. Human Capital Performance
Human Capital Performance assess staff competence, engagement, and retention. It highlights leadership effectiveness and team collaboration. Human Capital is measured through appraisals, feedback, and capacity-building outcomes.
4. Customer/Stakeholder Satisfaction
The dimension looks at the responsiveness to needs and expectations of customers and stakeholders. It uses trust, loyalty, and perceived value as it’s indicators.
5. Innovation & Adaptability.
This is the ability to respond to change and seize opportunities. Implementation of new ideas, technologies, or models are the key aspects on innovation and adaptability.
6. Strategic Alignment
It is the consistency with mission, vision, and long-term goals of the organization. It deals with the adherence to policies and ethical governance. According to the aspect performance is not just about doing things right—it’s about doing the right things.
7. Social & Environmental Impact
Here we look at the contribution to societal well-being and sustainability. It looks at how well the organization’s practices are ethical and how it engages the community.

Leave a comment